It’s hard when you’ve been through a difficult time (like we all have since the coronovirus landed), finally feel that you’re coming out of it, and then discover that the promised relief has suddenly been snatched away. That’s how the last three months has felt: with the lull in vaccinations, the resurgence of the virus, and the lingering impact on schools, work and the ability to keep your chin up.
I’m writing this on the 20th anniversary of 9/11, and the recaps around that day have been everywhere. I mostly stopped paying attention after the wake-up-call of one of them, Frontline’s review of the terrorist attack and the fear and disasters that followed (right down to the botched evacuation from Kabul’s airport two weeks ago). Their documentary, America After 9/11, made this passage of time feel “all of a piece,” twenty years when I’ve felt that we’ve mostly spiraled downward as a country, both here at home and out in the wider world.
It only made the cloud that was pressing down already feel that much heavier.
In thinking about recent debacles, I often “follow the money” as I look for the culprits in a saga like these post 9/11 years have been: the sheer, staggering cost to all of us (in dollars) and for more than a few of us (in post-traumatic stress, dismemberment, addiction, and lives lost on the battlefield or to suicide). For example, I realize that my daughter has known almost nothing other than these sad 20 years.
Perhaps numbed by these human costs, my alarm only escalated when I saw (as you saw) America leaving behind hundreds of millions of dollars of vehicles, weapons, equipment, uniforms, indeed whole military bases when we departed from Afghanistan and nobody, nobody seemed to have made a list of it all so those of us who had paid for it knew we’d left behind, what it had cost us, and why we thought it was “Ok” to just pass it on to the Taliban.
Trillions of dollars were apparently spent in our foreign wars since 9/11. What does that level of spending even mean? It numbs the mind until you start breaking it down and realize that the cost of a single Humvee could support a family down the street (wherever you live “in our homeland”) for a year or more. No one seems to want the public of you and me to know the specifics beyond these unfathomable cost estimates—because then, presumably, someone would have to be held accountable, like you would a thief who’s gotten into your house (or shop or school) and is made to empty his pockets, one item at a time.
It’s a convenient slight of hand—this vaporous expense—because the industry behind the war machine we’ve abandoned near Kabul stands to become even richer if we “ditch the old stuff” and get to make a newer, shinier, even more expensive war machine the next time around. Because after all, when we’re confronted with some new threat, we’ll say, as Americans always seem to say when we’re afraid: “Of course. Buy it. We’ll worry about whether we can afford it later.”
The cloud that presses down continues to grow as I appreciate how little discussion there’s been about this aspect of the bungled evacuation from Afghanistan, indeed our abandonment of all our post 9/11 nation-building and democracy-exporting efforts. The cloud further discombobulates when I realize that we’ll do it all over again if we don’t pause, re-think and ultimately re-group very differently as a result of these misadventures.
Of all people, it was Dwight Eisenhower, the Supreme Allied Commander during World War II and U.S. president during much of the 1950’s—this man who helmed our last great war—who said it most eloquently, perhaps because more than almost anyone he knew what he was talking about and had the gumption and stature to speak the truth. Something brand new had come out of WWII, a military-industrial complex, that was bigger and more worrisome than any commander-in-chief or even government could control. If we’re not mindful (Eisenhower warned), this new war machine will jeopardize the health of our country and its brightest prospects in the future.
Eisenhower put his warning into his farewell address to the nation at the end of his term—literally his last important words to us as president, and surely his most prophetic.
Until the latest of our world conflicts, the United States had no armaments industry. American makers of plowshares could, with time and as required, make swords as well. But now we can no longer risk emergency improvisation of national defense; we have been compelled to create a permanent armaments industry of vast proportions. Added to this, three and a half million men and women are directly engaged in the defense establishment. We annually spend on military security more than the net income of all United States corporations.
This conjunction of an immense military establishment and a large arms industry is new in the American experience. The total influence — economic, political, even spiritual — is felt in every city, every State house, every office of the Federal government. We recognize the imperative need for this development. Yet we must not fail to comprehend its grave implications. Our toil, resources and livelihood are all involved; so is the very structure of our society….
We must never let the weight of this combination endanger our liberties or democratic processes. We should take nothing for granted. Only an alert and knowledgeable citizenry can compel the proper meshing of the huge industrial and military machinery of defense with our peaceful methods and goals, so that security and liberty may prosper together.
Over the past 60 years, Eisenhower’s worst fears have largely been realized, their frightful impacts “economic, political, [and] even spiritual.”
Moreover, it bears noting that the military-industrial-complex has grown beyond the companies, consultants and influence peddlers that had already joined forces by the 1960s. For example, attempts are increasingly being made to integrate the Silicon Valley tech companies more closely into governmental functions like data capture, surveillance, cyber-security and cyber-warfare. (See “As Google, Microsoft and Amazon Seek Bigger Defense Role, Some are Leery,” an article that appeared in the Wall Street Journal on Tuesday of last week.)
Of course, there are several reasons for the alarming rise of disruptive, profit-oriented “power centers” like this and similar ones that seem to always want to slow dance with our government. There are also reasons we never get around to pushing them away. The same pharmaceutical industry that rips the public off in most years comes to our rescue with a revolutionary vaccine—so it can’t be that bad. The military-industrial-complex (or MIC) that gorges itself on billion-dollar defense budgets saves us from more terrorist attacks after 9/11, so it too can’t be that bad.
These periodic reprieves make us (and our elected representatives) seem to forget all the bad stuff for a while and we never find the will to do all the post-mortems that we (and they) should also be conducting–like why prescription drugs are orders-of-magnitude cheaper in Canada or Mexico, or why the entire American government seemed to be hoodwinked into the Iraq war by “weapons of mass destruction.” Any impetus for reigning in these industries seems to be undermined by their occasional but far-too-expensive star-turns as “national saviors.”
Moreover, a megadon like the MIC operates in and provides high-paying jobs in every US city, state and territory. Because it’s a manufacturing and job machine too, it makes regular and generous campaign contributions to every elected official where it operates as “a cost of doing business,” or, more accurately, as “a cost to keep the business coming.” Since most elected officials easily spend as much time fund-raising as governing, there are powerful financial incentives to refrain from “biting the hand that feeds them” and even cutting the MIC back down to where it already was when Eisenhower rang his alarm bell.
The difficulties of “oversight and management” of the MIC are further compounded by two other factors, locked without end into their own, counterproductive back-and-forth.
Millions of Americans work in companies that contribute to our seemingly perpetual war efforts (indeed, a few of you might be reading this now). Once again, it feels like “biting the hand that feeds you” to question the implications of your work, at least until your son comes home from war with traumatic brain injuries or you’re shocked into wondering “how it was all worth it” while watching something like our sad retreat from Kabul two weeks ago.
But even then, even with personal or citizen-based horror about the MIC’s impacts, the impetus to do something about it, to complain or protest, to agitate for a different way of conducting America’s affaris, is undermined (somewhat) by self-interest—it’s my paycheck, after all—but even more so by fear: fear that if “I” want our country to spend less, do less, dismantle the-worst-of-the-MIC, then when the next national security threat appears (because of course it will, and of course we won’t be ready for it), “I’ll” be blamed for wanting us to cut back on our so-called “defensive and offensive capabilities”—like failing to manage a winning football team effectively. This vague concern about complicity silences the better angels that tell us: surely, there are higher motivations than fear that WE COULD AND SHOULD be responding to as individuals, as communities and as a country.
It all seems too big to do much more than stew about. But isn’t awareness that you’re a drunk or an addict (with the MIC as your fear-reducing drug) the first step towards a cure?
Despite new news cycles about virus patients triaged in Idaho hospitals or our kids being afraid to go back to school, I’ve been trying to linger over the SYSTEMIC imbalances (I think the word is right when used here) that the military-industrial-complex has introduced into my life and work because it seems to me that much of my life and work would have been different (and better) these past 20 (or more) years if we’d been working to achieve different priorities as a country—priorities with aspirations like the moon-landing a few years after Eisenhower spoke—instead of whatever shell-game we’ve been playing ever since.
Awareness of how our national treasure and bandwidth are being spent is, I think, the first step towards choosing to spend these scarce commodities more judiciously.
For example, some of us want to de-fund the police to allocate energy and resources to other community priorities. I think it’s far more complicated than that because police departments are (among many other things) just the tip of the MIC iceberg. All you need to prove it is to see local police departments like ours in Pennsylvania taking to the streets with military grade equipment that they’ve gotten as surplus from our wars in Iraq and Afghanistan.
What we’re fighting, and shouldn’t be fighting, is all around us.
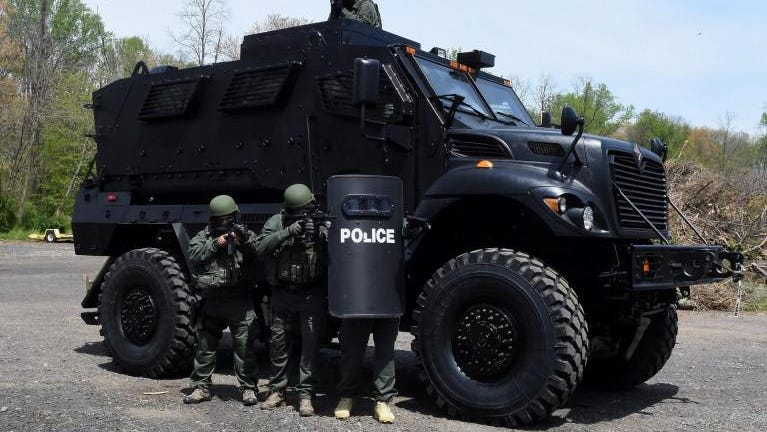

Pennsylvania police departments have received more than $6 millionin military ordinance over the past few years.
I’m writing about this particular cloud today because, eventually, we’ll learn how to manage Covid-19 more effectively and because our 24/7 news cycles suddenly stopped covering the incompetent way that we just evacuated ourselves out of our country’s longest war. Our whole, sad, 20-year experience in Iraq and Afghanistan, from beginning to bitter end, merits enough of our attention to reach at least the beginnings of a judgment—and maybe, several judgments about it.
I think our experience requires following the money and wondering whether the priorities we’ve been financing are really worth as much as we’ve been paying (economically, politically and even spiritually) for them: because in a world of limits, if you’re paying for one thing you’re NOT paying for some thing else—and bearing the opportunity costs.
As I sat down to write to you yesterday, on 9/11, my plan was to acknowledge the cloud I’ve been operating under (that maybe you have been operating under too) for the past month or so and point in a more optimistic direction. I wanted to look back with you from 2050 and glimpse the world that even now we’re beginning to create to meet the demands of a healthier, more sustainable planet. (Instead, I’ll do that next Sunday, in a Part 2-post.) But as you’re suspecting from my shift from the objectives of a military-industrial-complex to those of a carbon-reduced environment, our priorities will need to change as we stumble towards a different and more necessary future.
In the meantime, we’ll start to confront our financial limits, how much we can put on the credit card without a pay-off, what we can and cannot afford. Even in a fear-inducing world, a free society can only afford so much security—and, after all is said and done, HOW MUCH MORE SECURE DO YOU FEEL in the wake of our government’s flushing trillions of your dollars away? If we’re serious about healing our home-planet, we’ll have to “right-size” the military-industrial-complex that purports to protect our corner of it.
There’s simply no alternative.
It will be a messy, polarizing discussion, two steps forward and one back, with gridlock for years at a time (because that’s what a democracy does), but a debate about our biggest most expensive priorities may already have begun at the Kabul airport—and the more voices that join in that debate the better.
Follow where the money’s been spent and where new dollars are going. Priorities are realized with budgets and by those with the wisdom to guide those budgets into accountable actions.
The debate that we’ve been needing to have for at least 60 years may finally be getting started.
(By the way, the illustration up top of a human under a cloud, was created by Simone Golob.)
This post was adapted from my September 12, 2021 newsletter. Newsletters are delivered to subscribers’ in-boxes every Sunday morning and occasionally I post the content from one of them here. You can subscribe by leaving your email address in the column to the right.