For years now, I’ve been drawn to the mind of Robert D. Kaplan. It’s not that I’ve always agreed with him, but his insights have rarely failed to pull me in.
Maybe it’s for all the reasons that I wrote last week’s post, A Deeper Sense of Place is an Anchor in Turbulent Times. For much of his lengthy career, Kaplan has written about geography’s influence on politics and national power. He believes that where a people are located,” the place they “call home”—it’s proximity to powerful nations, it’s access to river systems, the extent of its undeveloped frontier, its natural resources (or lack of them), whether they’re protected by mountain ranges or oceans—has “a determining effect” on how these people view themselves and the world around them.
The importance of place was my way into Kaplan’s writing because, in my gut, I always felt he was right.
Three years ago, I wrote about a book by Kaplan called Earning the Rockies: How Geography Shapes America’s Role in the World (2017). It was another illuminating read. This was a time when the executives helming America’s tech companies were still using their prominence and financial clout to lecture the rest of us about “what progress should look like” from their ideological points of view. In that post, I wondered how their rugged individualism, honed on technology’s frontier, jived with Americans skepticism about ideologies and their commandments, another take-away from the “frontier mentality” that Kaplan ascribed to most Americans.
Frontiers [like America’s] test ideologies like nothing else. There is no time for the theoretical. That, ultimately, is why America has not been friendly to communism, fascism, or other, more benign forms of utopianism. Idealized concepts have rarely taken firm root in America and so intellectuals have had to look to Europe for inspiration. People here are too busy making money—an extension, of course, of the frontier ethos, with its emphasis on practical initiative…[A]long this icy, unforgiving frontier, the Enlightenment encountered reality and was ground down to an applied wisdom of ‘commonsense’ and ‘self evidence.’ In Europe an ideal could be beautiful or liberating all on its own, in frontier America it first had to show measurable results.
In the tumultuous years that have followed, my question has been answered in part by a populist, Know-Nothing revulsion aimed at “thought-leaders,” big-shots and experts of all kinds who think they know better.
So perhaps it’s not a coincidence that this same three years has brought Kaplan to the short essay that appeared in the Wall Street Journal this week. It’s called “The Tyranny of the 21st Century Crowd” and it came with the following elaboration: “Mobs that form from the bottom up may prove even harder to defeat than totalitarian regimes.” (Here’s a link that makes his essay available beyond the usual paywall.)
What does any of this have to do with our work next week, the work that all of us should be doing, or the over-all quality of our lives at this place and time? As it turns out, quite a lot.
I had dinner this past week with a small business owner whose office is indirectly buffeted on a regular basis by mob-related mentalities. One of his longtime employees—someone who happens to have an advanced degree—is from a family of anti-vaxers, refuses to send her child to a school that requires vaccinations, and is pushing hard for an accommodation to move her work (from live to remote) to another state where she thinks the schools will be more lenient. A second longtime employee is a member of two oppressed groups (based on age and on race). This employee apparently doesn’t feel like working any more, but also holds the implicit (if meritless) threat of a discrimination action if he is either disciplined or fired. Of course, getting an 8-hour workday out of either of these “disgruntled employees” has turned into a daily minefield.
I couldn’t help but sympathize.
Who needs the expense and aggravation of being dragged by either of these people into a courtroom because they believe (and therefore can claim, without evidence) that their employer is treating them unfairly by refusing to give them what they want?
How can my friend (indeed how can anyone) run a business today when employees can assert the abridgement to some freedom- or identity-based right when all he is demanding is that they come into the office and do the work that they’re being paid to do?
I got a close-to-the-ground view of the mobs that loomed behind my friend’s two employees over dinner this week. But beyond examples like these, Kaplan foresees today’s mob-based threats causing wider, deeper and even more troubling consequences for a way of living and working that we assume is far more resilient than it actually is.

Pavlov’s dog parade is by a favorite artist, the late cartoonist and social commentator Saul Steinberg. (If it looks familiar, I also featured it in my post, We’re All Acting Like Dogs Today, on the refusal by regulators (and the public behind them) to confront the user manipulation and mob tendencies that are an inherent feature of dominant tech platforms like Google.Twitter and Facebook.)
While Kaplan implicitly acknowledges the American peoples’ general hostility to foreign ideologies like communism and fascism, along with its “heartland’s” hostility to the progressive ideologies of the East and West Coasts, he certainly recognizes the populist impulses that bubble beneath all of these debates.
For Kaplan, the Peoples’ arguments over their deeply held political beliefs usually represent “a profound abasement of reason.” In other words, populists of all stripes generally feel the rightness of their views instead of reasoning themselves into the convictions that they hold. Under these circumstances, it’s difficult if not impossible to foresee how America willl be able to maintain its democratic way of life when every quadrant of our politics is being actively overtaken by its own version of a mob. (While Kaplan doesn’t delve into these divisions, George Packer recently described “the four political belief systems” that are operating in the U.S. today in “How America Fractured Into Four Parts,” an article of his that I discussed here in June.)
What Kaplan does do is quote liberally from a book about mobs that I’d never heard of: Crowds and Power by Elias Canetti.
The crowd, Canetti says, emerges from the need of the lonely individual to conform with others. Because he can’t exert dominance on his own, he exerts it through a crowd that speaks with one voice. The crowd’s urge is always to grow, consuming all hierarchies, even as it feels persecuted and demands retribution. The crowd sees itself as entirely pure, having attained the highest virtue.
Thus, one aim of the crowd is to hunt down the insufficiently virtuous. The tyranny of the crowd has many aspects, but Canetti says its most blatant form is that of the ‘questioner,’ and the accuser. ‘When used as an intrusion of power,” the accusing crowd ‘is like a knife cutting into the flesh of the victim. The questioner knows what there is to find, but he wants actually to touch it and bring it to light.’
The tyranny and violence of the mob reaches its crescendo when it exercises the monopoly that it believes it has on virtue. ‘If you don’t agree with us,’ Canetti says of them, ‘you are not only wrong but morally wanting, and as such should not only be denounced, but destroyed.’ Then he deploys notions about nations and their exercise of power to provide historical perspective as well as a glimpse into the future of America’s power. Where once America’s (and the West’s) power resided in its political, educational and media institutions and in the civic cohesion they produced, today that foundation is increasingly undermined not by counter-institutions (that seek social change for the better) but by mob power (whose primary interest is in weakening, when not actively seeking to destroy, the institutions that once bound us together).
Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union were defeated by U.S. military and industrial power. Civilizations rest not only on intellectual and cultural foundations but also on coarser aspects of strength and power. The historic West, which is ultimately about the freedom of the individual to rise above the crowd, survived the 20th century thanks to American hard power, itself maintained by a system of individual excellence in the arts and sciences, in turn nurtured by an independent and diverse media. But that media is now becoming immersed in the crowd, where it demands virtue in its purest ideological form, so that much of the media too often plays the role of Canetti’s accuser.
The lust for purity combined with the tyranny of social-media technology in the hands of the young—who have little sense of the past and of tradition—threatens to create an era of the most fearsome mobs in history. The upshot of such crowd coercion is widespread self-censorship: the cornerstone of all forms of totalitarianism….
This ultimately leads toward a controlled society driven by the bland, the trivial and the mundane, wearing the lobotomized face of CNN weekday afternoon television. Outright evil can surely be dealt with, but a self-righteous conformity is harder to resist. Left unchecked, this is how the West slowly dies.
The self-censorship that this kind of tyranny causes and the masks it forces us to wear are more isolating than any restrictions that were imposed during the pandemic. Reasonable people withdraw from free exchange for fear of having their livelihoods and reputations challenged by self-righteous mobs. Effectively “lobotimizing ourselves,” we mask up to avoid being “destroyed.”

One of the Saul Steinberg and Inge Morath images from The Mask Series (1959-1963).
Reading Kaplan’s essay reminded me of a book that I hadn’t read since college, The Revolt of the Masses by Orega y Gasset, a Spanish essayist.
Sounding like an Old Testament prophet 85 years ago, Ortega wrote about the undermining of “liberalism” by mobs of communist and right-wing agitators. He feared the “tyranny of [any] majority” and the “collective mediocrity” of the “masses” (and the so-called “mass-men” that populated them). Ortega believed they threatened both individuality and freedom of thought with annihilation. Much like Kaplan, he wrote:
The mass crushes beneath it everything that is different, that is excellent, individual, qualified, and select. Anybody who is not like everybody, who does not think like everybody, runs the risk of being eliminated. And it is clear that this ‘everybody’ is not ‘everybody.’ ‘Everybody’ was normally the complex unity of the mass and the divergent, specialized elite groups. Nowadays, ‘everybody’ is the mass alone.
Twenty years later, in Homage to Catalonia (George Orwell’s sobering account of his own time fighting for the Republicans during the Spanish Civil War), the eventual author of 1984 and Animal Farm reached the same conclusion as Ortega about the mobs of the left and the right that were squeezing the life blood our of their homeland. It was an experience that eviserated the romanticism that an idealistic young man had once felt for his own republican principles.
Even with their differences, Orwell, Ortega and Kaplan would probably agree that it was the power of America and the West—the only champions of “liberal” values left standing—that liberated at least some of the civilized world from the mobs that were overtaking it before World War II. As we sit here today, it’s hardly misplaced to wonder: Who, if anyone, will do so again?
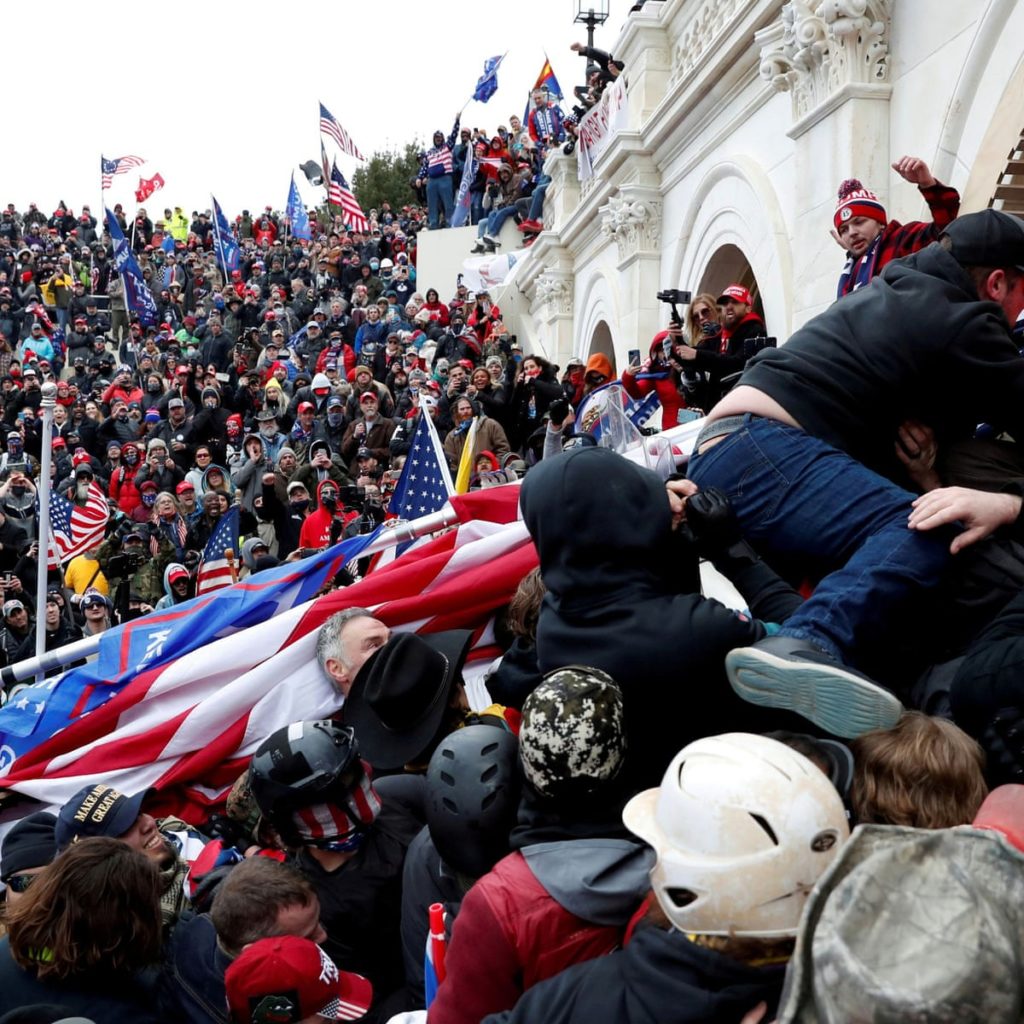

In the course of his essay, Robert Kaplan doesn’t mention the mob that attempted to interrupt the Electoral College vote in Washington last January; not a woke mob enforcing its virtue from prominent positions in the nation’s media and universities, but a MAGA mob that was encouraged by a president who’d just been defeated at the polls.
The “insurrection” was another side of the same coin.
In a post from a month before the Capitol assault, I wrote about “the big lie” that was told to the German people following their defeat in World War I. “You didn’t actually lose,” conspiracists told them. “Our terrible surrender was the result of a plot by leftists, Jews, bankers and others who stood to gain from it.” That it was a lie hardly mattered, because it fed so seamlessly into the resentment, anger and economic hardship that many German soldiers, their families and communities were already feeling. It was these “regular people” who fed the mobs that led to national socialism and, only twenty years later, a second world war.
I think the wrong question to take from these historical similarities is whether Donald Trump is another Adolf Hitler. Instead, as I wrote a year ago:
Are there genuine parallels between Germany in the 1920s and 30’s and the U.S in the 2020’s and 30’s?
Were there political leaders (both then and now) who were willing to tell “a big, almost preposterous lie” if it could stoke existing grievances and rally their supporters so they could gain additional power?
Did the German people permit their leaders to send fellow Germans who were supposedly to blame for their tribulations to concentration camps?
How could so many free people, who had enjoyed democracy and the right to determine their futures, been overtaken by such a lie?
Surely, they knew then (as we know now) what was happening around them, as reporters today are called ‘enemies of the state’ and election officials are targeted for assassination.
Did they pretend (and are we pretending now) not to see the breakdowns in the fabric of our society that continue and only seem to get worse?
To paraphrase [the poet, W.H.] Auden: “Did the best among us on both sides really lack conviction, while only the worst / were full of passionate intensity”?
In a new HBO documentary about last January’s revolt of the masses, called “Four Hours at the Capitol” (link to the film’s trailer), a police officer who was interviewed recalled a piece of advice that he had gotten during his military training as he thought back to where he found himself that day:
Individuals aren’t usually a problem. But when they get together and create a mob, then, the mob is the weapon.
Too few in America and in the West today are actively trying to disarm these weapons, which are being stoked every day by social media, by too many in the legacy media, and by the demagogues who give voice to every flavor of them.
Will we need the purifying force of another world war—another battle to the death for the best and against the worst in our civilization—in order to break the hold that mob rule increasingly exerts over our politics, our freedom of speech, and our ability to be anything more than mass-men or -women in one frenzied crowd or another?
Maybe Kaplan and his intellectual forebears give us an alternative vision to hold onto: a view of America and the West that once again has the fortitude to stand up against every kind of mob in the world–not because of our theoretical beliefs about democracy and our Enlightenment traditions, but because we cherish our freedom and individuality for their practical benefits and refuse to give them up because weapons keep being pointed in our direction.
This post was adapted from my October 17, 2021 newsletter. Newsletters are delivered to subscribers’ in-boxes every Sunday morning and occasionally I post the content from one of them here. You can subscribe by leaving your email address in the column to the right.