
I’m frequently reminded about how oblivious I am, but I had a particularly strong reminder recently. I was in a room with around 30 other people watching a documentary that we’d be discussing when it was over. Because we’d all have a chance to share our strongest impressions and it was a group I cared about, I paid particularly close attention. I even jotted down notes from time to time as something hit me. After the highly emotional end, I led off with my four strongest reactions and then listened for the next half hour while the others described what excited or troubled them. Most startling was how many of their observations I’d missed altogether.
Some of the differences were understandable, why single “eye witness accounts” are often unreliable and we want at least 8 or 12 people on a jury to be sharing their observations during deliberations. No one catches everything, even when you’re watching closely and trying to be insightful later on. Still, I thought I was better at this.
Missing key details and reaching the wrong (or woefully incomplete) conclusions affects much of our work and many of our relationships outside of it. Emotion blinds us. Fear inhibits us from looking long and hard enough. Bias makes us see what we want to see instead of what’s truly there. To get better at noticing involves acknowledging each of these tendencies and making the effort to override them. In other words, it involves putting as little interference as possible between us and what’s staring us in the face.
As luck would have it, a couple of interactive challenges involving our perceptive abilities crossed my transom this week. Given how much I missed in the documentary, I decided to play with both of them to see if looking without prior agendas or other distractions actually improved my ability to notice what’s in front of me. It was also a nice way to take a break from our 24-7 free-for-all in politics. As I sat down to write to you, I thought you might enjoy a brief escape into “how much you’re noticing” too.
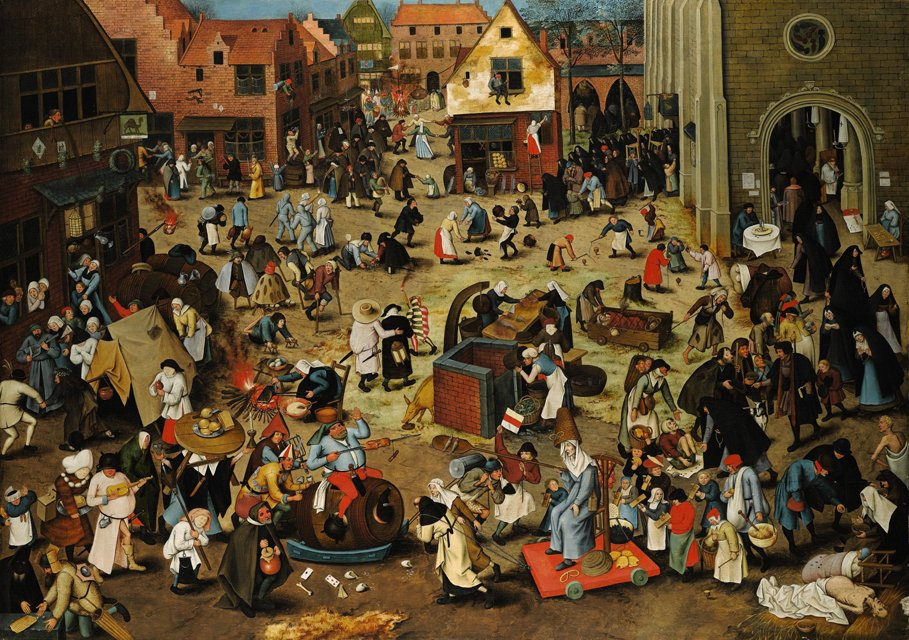
The Pieter Bruegel painting above–called “The Battle Between Carnival and Lent”–is currently part of the largest-ever exhibition of the artist’s work at Vienna’s Kunsthistoriches Museum. Bruegel is a giant among Northern Renaissance painters but most of his canvases are in Europe so too few of us have actually seen one, and when we have, they’ve been in books where it’s all but impossible to see what’s actually going on in them. As it turns out, we’ve been missing quite a lot.
Conveniently, the current survey of the artist’s work includes a website that’s devoted to “taking a closer look,” including how Bruegel viewed one of the great moral divides of his time: between the anything goes spirit of Carnival (the traditional festival for ending the winter and welcoming the spring) and the tie-everything-down season of Lent (the interval of Christian fasting and penance before Good Friday and Easter). “The Battle Between Carnival and Lent” is a feast for noticing, and we’ll savor some of the highlights on its menu below.
First though, before this week I’d never heard about people who are known as “super recognizers.” They’re a very small group of men and women who can see a face (or the photo of one) and, even years later, pick that face out of a crowd with startling speed and accuracy. It’s not extraordinary memory but an entirely different way of reading and later recognizing a stranger’s face.
I heard one of these super recognizers being interviewed this week about his time tracking down suspects and missing persons for Scotland Yard. His pride at bringing a remarkable skill to a valuable use was palpable–the pure joy of finding needles in a succession of haystacks. His interviewer also talked about a link to an on-line exercise for listeners to discover whether they too might be super recognizers. In other words, you can find out how good you are “with faces” and how well you stack up with your peers at recognizing them later on by testing your noticing skills here. Please let me know whether I’ve helped you to find a new and, from all indications, highly rewarding career. (The test’s administrators will be following up with you if you make the grade.)
Now back to Bruegel.

You can locate this central scene in “The Battle Between Carnival and Lent” in the lower middle range of the painting. Zooming in on it also reveals Bruegel’s greatest innovation as a painter. He gives us a birds-eye view of the full pageant of life that embraces his theme. It’s not the entire picture of “what it was like” in a Flemish town 500 years ago, but viewers had never before been able to get this close to “that much of it” before.
It’s also a canvas populated by peasants and merchants as opposed to saints and nobles. They are alone or in small groups, engaged in their own distinct activities while seemingly ignoring everyone else. In the profusion of life, it’s as if we dropped into the center of any city during lunch hour to eavesdrop.
The painting’s details show a figure representing Carnival on the left. He’s fat, riding a beer barrel and wearing a meat pie as a headdress. Clearly a butcher—from the profession that enabled much of the festival’s feasting—he holds a long spit with a roasted pig as his weapon for the battle to come. Lent, on the other hand, is a grim and gaunt male figure dressed like a nun, sitting on a cart drawn by a monk and real nun. The wagon holds traditional Lenten foods like pretzels, waffles and mussels, and Lent’s weapon of choice is an oven paddle holding a couple of fish, an apparent allusion to the parable of Jesus multiplying the loaves and the fishes for a hungry crowd. On one level then, the fight is over what we should eat at this time of year.
As the eye wanders beyond the comic joust, Carnival’s vicinity includes a tavern filled with revelers, on-lookers watching a popular farce called “The Dirty Bride” (that’s surely worth a closer look!) and a procession of lepers led by a bagpiper. On the other hand, Lent’s immediate orbit shows townsfolk drawing water from the well, giving alms to the poor and going to church (their airs of generosity equally worthy of closer attention).
Not unlike our divided society today, Bruegel painted while the battle for souls during the Reformation was on-going, but instead of taking sides, this painting seems to take an equal opportunity to mock hypocrisy, greed and gluttony wherever he found it, making this and others of his paintings among the first images of social protest since Romans scrawled graffiti on public walls 1200 years before. While earlier paintings by other artists carefully disguised any humor, Bruegel wants you to laugh with him at this spectacle of human folly.
It’s been argued that Bruegel also brings a more serious purpose to his light heartedness, criticizing the common folk by personifying them as a married couple guided by a fool with a burning torch—an image that can be found in almost in the exact center of the painting. The way they are being led suggests that they follow their distractions and baser instincts instead of reason and good judgment. Reinforcing the message is a rutting pig immediately below them (you can find more of him later), symbolizing the destruction that oblivious distraction can leave in its wake.

Everywhere else Bruegel invites his viewers to draw their own conclusions. You can follow this link and notice for yourself the remarkable details of this painting along with others by the artist. Navigate the way that you would on a Google Map, by clicking the magnifying glass (+) or (-) to zoom in and out, while dragging your cursor to move around the canvas. Be sure to let me know whether you happen upon any of the following during your exploration (the circle dance, the strangely-clad gamblers with their edible game board, the man emptying a bucket on the head of a drunk) and whether you think Carnival or Lent seems to have won the battle.
Before wishing you a good week, I have a final recommendation that brings what we notice (say in a work of art) back to what we notice or fail to notice about one another every day.
The movie Museum Hours is about the relationship that develops between an older man and woman shortly after they meet. Johann used to be a road manager for a hard-rock band but now is a security guard at the same museum in Vienna that houses the Bruegel paintings. Anne has traveled from Canada to visit a cousin who’s been hospitalized and meets Johann as she traverses a strange city. During her visit, he becomes her interpreter, advocate for her cousin’s medical care, and eventually her tour guide. But just as he finds “the spectacle of spectatorship” at the museum “endlessly interesting” as he takes it in everyday, they both find the observations that they make about one another in the city’s coffee shops and bistros surprising and comforting.
Museum Hours is a movie about the rich details that are often overlooked in our exchanges with one another and that a super observer like Bruegel brings to his examination of everyday life. One of the film’s many reveals takes place in a scene between a tour guide at the museum (who is full of her own insights) and a group of visitors with their unvarnished interpretations in front of “The Battle Between Carnival and Lent” and other Bruegel paintings. You can view that film clip here, and ask yourself whether the guide is helping the visitors to see what is in front of them or diverting their attention away from it.
As we shuttle between two adults in deepening conversation and very different kinds of exchanges across Vienna, Museum Hours asks several questions, including what any of us hopes to gain from looking at famous paintings on the walls of a museum. As one of the movie’s reviewers wondered:
“Is it to look at fancy paintings and feel cultured, or is it to experience something more direct: to dare to unsheathe oneself of one’s expectations and inhibitions, and truly embrace what a work of art can offer? And then, how could one carry that open mindset to embrace all of life itself? With patient attention and quiet devotion, these are challenges that this film dares to tackle.”
That much open-mindedness is a heady prescription, and probably impossible to manage. But sometimes it’s good to be reminded about how much we’re missing, to remove at least some of our blinders, and to discover what we can still manage to notice when we try.
Note: this post was adapted from my October 14, 2018 Newsletter.


 It was great to hear from several of you after recent posts about defending your reputation “as a good person” when it’s challenged. Thanks, as always, for reaching out and letting me know what you think.
It was great to hear from several of you after recent posts about defending your reputation “as a good person” when it’s challenged. Thanks, as always, for reaching out and letting me know what you think.






 The book cover for “We Fed An Island” shows Andres holding a huge spatula and looking like he’s cooking. During his interview, he admitted that he didn’t do much cooking in Puerto Rico because his ability to manage the ever-changing demands was far more critical, “So, yes, my team probably is joking on these photos, saying, OK, the only time you would really cook [is when your picture is being taken].” Instead, his abilities enabled others to lead once he had gathered the raw materials and secured the facilities where they could do so. (“I became the leader, “ he said. “But actually, we had 25,000 leaders.”) As he later wrote:
The book cover for “We Fed An Island” shows Andres holding a huge spatula and looking like he’s cooking. During his interview, he admitted that he didn’t do much cooking in Puerto Rico because his ability to manage the ever-changing demands was far more critical, “So, yes, my team probably is joking on these photos, saying, OK, the only time you would really cook [is when your picture is being taken].” Instead, his abilities enabled others to lead once he had gathered the raw materials and secured the facilities where they could do so. (“I became the leader, “ he said. “But actually, we had 25,000 leaders.”) As he later wrote: